U-Boot/de
From Openmoko
(→Bootloader development) |
Marko Knöbl (Talk | contribs) m (Bootloader/de moved to U-Boot/de) |
||
| (39 intermediate revisions by 9 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| + | {{Languages|U-Boot}} | ||
| + | |||
[[Image:GTA01-U-Boot.JPG|thumb|300px|u-boot on Neo1973 console]] [[Image:Neo1973 uboot splash closeup.jpg|thumb|300px|u-boot boot splash on Neo1973]] | [[Image:GTA01-U-Boot.JPG|thumb|300px|u-boot on Neo1973 console]] [[Image:Neo1973 uboot splash closeup.jpg|thumb|300px|u-boot boot splash on Neo1973]] | ||
== Phase0 Schnellstart == | == Phase0 Schnellstart == | ||
| − | * Überprüfen, dass die Batterie eingebaut ist und | + | * Überprüfen, dass die Batterie eingebaut ist und das USB Kabel innerhalb der letzten 30 Sekunden nirgendwo angeschlossen war. |
* Das Neo (nicht das Debug Board) an einen Linux Rechner mit dem USB Kabel anschließen. | * Das Neo (nicht das Debug Board) an einen Linux Rechner mit dem USB Kabel anschließen. | ||
* Gleichzeitig die AUX und Power-up gedrückt halten, um ins Bootmenü zu gelangen. | * Gleichzeitig die AUX und Power-up gedrückt halten, um ins Bootmenü zu gelangen. | ||
| Line 14: | Line 16: | ||
Das GTA01 nutzt den [http://u-boot.sourceforge.net/ u-boot] Bootlader. | Das GTA01 nutzt den [http://u-boot.sourceforge.net/ u-boot] Bootlader. | ||
| − | Mehr Informationen | + | Mehr Informationen zu u-boot finden Sie unter |
* http://www.denx.de/wiki/DULG | * http://www.denx.de/wiki/DULG | ||
* http://www.gumstix.org/tikiwiki/tiki-index.php?page=U-Boot | * http://www.gumstix.org/tikiwiki/tiki-index.php?page=U-Boot | ||
| Line 32: | Line 34: | ||
== Bootlader Quellcode == | == Bootlader Quellcode == | ||
| − | Die aktuellen Patches des | + | Die aktuellen Patches des Bootladers sind zu finden unter http://svn.openmoko.org/trunk/src/target/u-boot/patches/. |
| − | Entpacken Sie die Quellen, wenden Sie den Patch an, | + | Entpacken Sie die Quellen, wenden Sie den Patch an, führen Sie "make gta01bv3_config" (oder "gta01bv2_config" bzw. die entsprechende Hardwareversion) aus und führen Sie "make" aus. |
Als Resultat erhalten sie die Binärdatei "u-boot.bin", welche Sie direkt (entweder mit dem vorhandenen Bootlader oder [[sjf2410-linux]]) in den NAND Flash Speicher laden können. | Als Resultat erhalten sie die Binärdatei "u-boot.bin", welche Sie direkt (entweder mit dem vorhandenen Bootlader oder [[sjf2410-linux]]) in den NAND Flash Speicher laden können. | ||
== Bootlader Binärdatei == | == Bootlader Binärdatei == | ||
| − | + | Das aktuellste Binärimage des Bootladers finden Sie unter http://downloads.openmoko.org/daily/ . Dieses sollte auf die Adresse 0x00000000 im NAND Flashspeichers geschrieben werden (Größe 0x30000). | |
== Bootloader Entwicklung == | == Bootloader Entwicklung == | ||
=== QT2410 === | === QT2410 === | ||
| − | + | Wenn Sie de Entwicklung des Bootladers unter QT2410 betreiben möchten, dann ist es einfacher, mit einem Bootlader Image zu arbeiten, das per USB ins Ram geflasht werden kann. | |
| − | + | Um dies zu tun, müssen Sie die Datei u-boot/include/configs/qt2410.h editieren ("if 0" in der Zeile 32 auf "if 1" ändern) und danach mit "make" neu übersetzen. | |
| − | + | Die resultierende Datei "u-boot.bin" ist _NICHT_ für NAND verwendbar, sondern nur direkt im RAM, indem Sie z.B. das Programm [[s3c2410_boot_usb]] verwenden. | |
=== GTA01 === | === GTA01 === | ||
| − | + | Bootlader Entwicklung unter GTA01 ist etwas trickreich. Zuerst gibt es keinen NOR Flash. Weiterhin gibt es aber keine andere Weise vom NAND zu laden. Folglich haben wir keinen USB Downloader wie das QT2410. | |
| − | + | Das Hauptproblem ist: Das [[S3C2410 Steppingstone]] kopiert unbedingt die ersten 4k des Flashes ins interne SRAM. Das SRAM Segment bleibt an der physischen Adresse allerdings auf null. | |
==== Nutzen des JTAG zum Booten aus dem RAM ==== | ==== Nutzen des JTAG zum Booten aus dem RAM ==== | ||
| − | So | + | So, wie kann man nun vom RAM booten? Dazu nutzt man JTAG / OpenOCD, um |
| − | * | + | * Zurücksetzen und Halten der CPU auf PC=0 |
<pre> | <pre> | ||
> reset halt | > reset halt | ||
| Line 68: | Line 70: | ||
</pre> | </pre> | ||
| − | * | + | * Herunterladen eines kleinen Stückes Code vom SRAM (4k SRAM von Steppingstone überschreiben). |
<pre> | <pre> | ||
> load_binary /space/misc/gta01/u-boot.git/board/gta01/lowlevel_foo.bin 0 | > load_binary /space/misc/gta01/u-boot.git/board/gta01/lowlevel_foo.bin 0 | ||
| Line 74: | Line 76: | ||
</pre> | </pre> | ||
| − | * | + | * Setzen einer Sprungmarke an der Adresse 0x33f80000 (was anzeigt, dass das low-level Code an dieser Stelle endet) |
<pre> | <pre> | ||
> bp 0x33f80000 4 hw | > bp 0x33f80000 4 hw | ||
| Line 80: | Line 82: | ||
</pre> | </pre> | ||
| − | * | + | * Den Code bis zur Sprungmarke ausführen |
<pre> | <pre> | ||
> resume | > resume | ||
| Line 90: | Line 92: | ||
</pre> | </pre> | ||
| − | * | + | * Das u-boot Image auf die Ardesse 0x33f80000 laden |
<pre> | <pre> | ||
> load_binary /space/misc/gta01/u-boot.git/u-boot.bin 0x33f80000 | > load_binary /space/misc/gta01/u-boot.git/u-boot.bin 0x33f80000 | ||
| Line 96: | Line 98: | ||
</pre> | </pre> | ||
| − | * | + | * Ausführung fortsetzen |
<pre> | <pre> | ||
> resume | > resume | ||
| Line 102: | Line 104: | ||
</pre> | </pre> | ||
| − | + | Ab diesem Punkt wird die Hintergrundbeleuchtung hell und man sieht folgende vertraute Kommandozeilenaufforderung auf der seriellen Konsole. | |
<pre> | <pre> | ||
U-Boot 1.1.6 (Jan 13 2007 - 23:44:23) | U-Boot 1.1.6 (Jan 13 2007 - 23:44:23) | ||
| Line 117: | Line 119: | ||
</pre> | </pre> | ||
| − | == | + | == Erzeugen der bootbaren Images == |
| − | u-boot | + | u-boot benötigt bootbare Images (wie der Kernel, aber auch initrd und andere) in Form des sogenannten ''uImage''. Um ein ''uImage'' von z.B. einem ''vmlinuz'' zu erzeugen, kann man wie folgt vorgehen: |
<pre> | <pre> | ||
objcopy -O binary -R .note -R .comment -S vmlinux linux.bin | objcopy -O binary -R .note -R .comment -S vmlinux linux.bin | ||
gzip -9 linux.bin | gzip -9 linux.bin | ||
| − | u-boot/tools/mkimage -A arm -O linux -T kernel -C gzip -a 30008000 -e 30008000 -n "Kernel Image QT2410" -d linux.bin.gz uImage | + | u-boot/tools/mkimage -A arm -O linux -T kernel -C gzip -a 30008000 -e 30008000 \ |
| + | -n "Kernel Image QT2410" -d linux.bin.gz uImage | ||
</pre> | </pre> | ||
| − | == | + | == Bootmenü == |
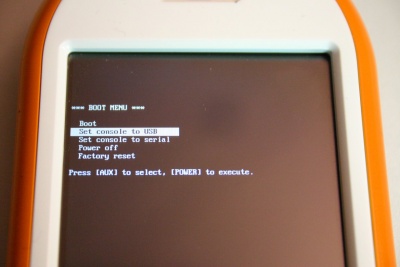
[[Image:Neo1973 uboot menu.jpg|thumb|400px|u-boot boot menu on Neo1973]] | [[Image:Neo1973 uboot menu.jpg|thumb|400px|u-boot boot menu on Neo1973]] | ||
| − | + | Ab dem Phase-0 Release zeigt jetzt unsere u-boot Version ein Bootmenü auf dem Startbildschirm an. | |
| − | === | + | === Zugriff auf das Bootmenü === |
| − | + | Um ins Bootmenü zu gelangen, müssen Sie gleichzeitig den [[Neo1973 AUX Button]] und den Power Button gedrückt halten. | |
| − | === | + | === Nutzung des Bootmenü === |
| − | + | Mit dem [[Neo1973 AUX Button]] können Sie zwischen den Menüoptionen wechseln. Mit dem ''POWER'' Button wählen Sie eine Option aus. | |
| − | === | + | === Hunzufügen von Menüpunkten zum Bootmenü === |
| − | + | Sie können weitere Optionen zum Bootmenü hinzufügen indem Sie Umgebungsvariablen setzen. Die kanonische Form ist ''menu_<number> <Title>: U-Boot-Commands'' | |
| − | + | Zum Beispiel fügt folgender Befehl einen Menüeintrag, der auf das Schnellladen schaltet und die Hintergrundbeleuchtung deaktiviert: | |
setenv menu_6 Autofast-Charge and Backlight Off: neo1973 charger autofast\; neo1973 backlight off | setenv menu_6 Autofast-Charge and Backlight Off: neo1973 charger autofast\; neo1973 backlight off | ||
saveenv | saveenv | ||
| − | + | In diesem Zustand kann das Neo1973 mit einem üblichen USB Ladegerät aufgeladen werden. Sie müssen allerdings 'setenv boot_menu_timeout 65000' setzen, um das Abschalten zu verhindern. | |
| − | == | + | == Bootlader Kommandozeile == |
| − | === | + | === Zugriff auf den Bootlader Prompt === |
| − | + | Der Bootlader Prompt steht entweder auf einer seriellen Konsole (über [[Debug Board]]) oder als virtuelles serielle USB Gerät ([[CDC ACM|USB CDC_ACM]]) zur Verfügung. Ob serielle Schnittstelle oder USB Port verwendet werden, hängt von den u-boot Umgebungsvariablen '''stdin''', '''stdout''' und '''stderr''' ab. | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | Unabhängig davon, ob Sie usbtty nutzen oder nicht, die ersten Nachrichten werden immer auf der seriellen Konsole angezeigt. | |
| − | + | Der Bootlader ist so konfiguriert, dass er drei Sekunden wartet. Wenn innerhalb dieser drei Sekunden eine Taste auf '''stdin''' gedrückt wird, wird der automatische Bootvorgang abgebrochen. | |
| − | ==== | + | ==== Nutzung von usbtty unter Linux ==== |
| − | + | Durch den Anschluss des Neo im u-boot Modus am PC, sollte ein [[CDC ACM]] Gerät erkannt werden und Sie können ihn über /dev/ttyACM0 ansprechen. Wenn nicht, aktivieren Sie die CONFIG_USB_ACM Unterstützung (Device Drivers -> USB support -> USB Modem (CDC ACM) support). Anleitungen für MaxOS X User befinden sich [[MacOS_X#USB_Serial|hier]]. | |
| − | + | Für den Zugriff verwenden Sie Ihren bevorzugten Terminalemulator (minicom, cu, zc, screen ...) wie auf jede andere serielle Schnittstelle. Wenn Sie keinen Favoriten haben, versuchen Sie es einfach: | |
cu -l /dev/ttyACM0 | cu -l /dev/ttyACM0 | ||
| − | + | Eventuell ist folgender Befehl notwendig: | |
chown uucp.uucp /dev/ttyACM0 | chown uucp.uucp /dev/ttyACM0 | ||
| − | + | um die erforderlichen Rechte zu erhalten (auch als root). | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| + | Zuerst sollten Sie prüfen, ob das USB Gerät wärend des u-boot Modus in 'lsusb' angezeigt wird: | ||
# lsusb -d 1457:5119 | # lsusb -d 1457:5119 | ||
Bus 005 Device 079: ID 1457:5119 | Bus 005 Device 079: ID 1457:5119 | ||
| − | + | Als zweites können weitere Informationen über das Endgerät und deren Konfiguration angezeigt werden: | |
| − | + | ||
<pre> | <pre> | ||
# lsusb -v -d 1457:5119 | # lsusb -v -d 1457:5119 | ||
| Line 193: | Line 193: | ||
idProduct 0x5119 | idProduct 0x5119 | ||
bcdDevice 0.00 | bcdDevice 0.00 | ||
| − | iManufacturer 1 | + | iManufacturer 1 Openmoko, Inc |
iProduct 2 Neo1973 Bootloader U-Boot 1.2.0-g6c7cac8c-dirty-moko3 | iProduct 2 Neo1973 Bootloader U-Boot 1.2.0-g6c7cac8c-dirty-moko3 | ||
iSerial 3 0000000 | iSerial 3 0000000 | ||
| Line 281: | Line 281: | ||
</pre> | </pre> | ||
| − | + | Als nächstes können Sie es mit einem beliebigen Terminal Programm nutzen. | |
| − | + | Wenn die Umgebung nicht richtig gesetzt ist, dann müssen Sie die aktuelle Konsole nutzen (z.B. serielle Konsole) um sie zu setzen: | |
<pre> | <pre> | ||
GTA01Bv2 # setenv stderr usbtty | GTA01Bv2 # setenv stderr usbtty | ||
| Line 290: | Line 290: | ||
</pre> | </pre> | ||
| − | ==== | + | ==== Typischer u-boot Prompt ==== |
<pre> | <pre> | ||
| Line 307: | Line 307: | ||
</pre> | </pre> | ||
| − | === | + | === Kommandos auf dem Bootlader Prompt === |
==== Auto-boot ==== | ==== Auto-boot ==== | ||
| − | Auto-boot | + | Auto-boot führt in der Umgebungsvariable ''bootcmd'' definierte Kommandos aus. Standard Konfiguration ist: |
<pre> | <pre> | ||
GTA01Bv3 # printenv | GTA01Bv3 # printenv | ||
| Line 317: | Line 317: | ||
</pre> | </pre> | ||
| − | + | Dies bedeutet, dass es versucht wird zuerst die NAND Partition '''kernel''' in die Speicheradresse 0x32000000 zu kopieren und und sie dann zu starten. | |
| − | ==== | + | ==== Umgebung ==== |
| − | u-boot | + | u-boot ist konfiguriert, um die Umgebung im nichtflüchtigen NAND Flash Speicher zu verwalten. Sie können folgende Kommandos nutzen, um die Umgebung zu lesen, verändern oder zu speichern: |
<pre> | <pre> | ||
GTA01Bv2 # printenv | GTA01Bv2 # printenv | ||
| Line 351: | Line 351: | ||
</pre> | </pre> | ||
| − | + | Hinweis: Wenn mehrere Kommandos gesetzt sind, z.B. für bootcmd, dann sind Trennzeichen ';' notwendig, zum Beispiel | |
| − | + | ||
<pre> | <pre> | ||
GTA01Bv3 # setenv bootcmd mmcinit\; ext2load mmc 0 0x32000000 uImage\; bootm 0x32000000 | GTA01Bv3 # setenv bootcmd mmcinit\; ext2load mmc 0 0x32000000 uImage\; bootm 0x32000000 | ||
| Line 359: | Line 358: | ||
==== MMC/SD ==== | ==== MMC/SD ==== | ||
| − | + | Zur Initialisierung einer MMC/SD Karte, müssen Sie das Kommando ''mmcinit'' nutzen: | |
<pre> | <pre> | ||
GTA01Bv3 # mmcinit | GTA01Bv3 # mmcinit | ||
| Line 375: | Line 374: | ||
</pre> | </pre> | ||
| − | + | Danach kann ein ext2 Dateisystem gelesen werden: | |
<pre> | <pre> | ||
GTA01Bv3 # ext2ls mmc 0 | GTA01Bv3 # ext2ls mmc 0 | ||
| Line 402: | Line 401: | ||
</pre> | </pre> | ||
| − | ===== | + | ===== Laden des Kernels aus dem NAND ===== |
<pre> | <pre> | ||
| Line 410: | Line 409: | ||
GTA01Bv3 # bootm 0x32000000 | GTA01Bv3 # bootm 0x32000000 | ||
## Booting image at 32000000 ... | ## Booting image at 32000000 ... | ||
| − | Image Name: | + | Image Name: Openmoko Kernel Image Neo1973 |
Created: 2007-02-15 23:54:18 UTC | Created: 2007-02-15 23:54:18 UTC | ||
Image Type: ARM Linux Kernel Image (gzip compressed) | Image Type: ARM Linux Kernel Image (gzip compressed) | ||
| Line 421: | Line 420: | ||
</pre> | </pre> | ||
| − | ===== | + | ===== Neuen Bootlader ins NAND schreiben ===== |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| + | Folgende Kommandofolge lädt die Datei u-boot.bin aus dem ext2/mms und flasht diese in die Bootlader Flash Partition: | ||
<pre> | <pre> | ||
GTA01Bv3 # ext2load mmc 0 0x32000000 u-boot.bin | GTA01Bv3 # ext2load mmc 0 0x32000000 u-boot.bin | ||
| Line 432: | Line 429: | ||
</pre> | </pre> | ||
| − | ===== | + | ===== Neuen Kernel ins NAND schreiben ===== |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| + | Folgende Kommandofolge lädt die Datei ''uImage'' aus dem ext2/mmc und flasht sie in die Kernel Flash Partition: | ||
<pre> | <pre> | ||
GTA01Bv3 # ext2load mmc 0 0x32000000 uImage | GTA01Bv3 # ext2load mmc 0 0x32000000 uImage | ||
| Line 443: | Line 438: | ||
</pre> | </pre> | ||
| − | ===== | + | ===== Neues Hauptdateisystem (rootfs) ins NAND schreiben ===== |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| + | Folgende Kommandofolge lädt die Datei rootfs.jffs2 aus dem ext2/mmc und flasht sie in die rootfs Flash Partition: | ||
<pre> | <pre> | ||
GTA01Bv3 # ext2load mmc 0 0x32000000 rootfs.jffs2 | GTA01Bv3 # ext2load mmc 0 0x32000000 rootfs.jffs2 | ||
| Line 454: | Line 447: | ||
</pre> | </pre> | ||
| − | + | Bitte beachten Sie, dass dies nur mit root-Dateisystem Größen funktioniert, die kleiner sind als die Größe des Speichers vor 0x32000000, der im Falle von 64MB SDRAM ungefähr 32MB groß ist. | |
| − | ==== Neo1973 | + | ==== Unter Neo1973 verfügbare Kommandos ==== |
| − | + | Unsere Version von u-boot unterstützt eine Reihe von Neo1973 spezifischen Befehle: | |
<pre> | <pre> | ||
GTA01Bv2 # help neo1973 | GTA01Bv2 # help neo1973 | ||
| Line 473: | Line 466: | ||
</pre> | </pre> | ||
| − | + | Was ist das udc? | |
===== Timeouts ===== | ===== Timeouts ===== | ||
| − | + | Wenn das Bootlader Menü angezeigt wird, wird das Telefon ausgeschaltet, falls eine Weile keine Aktivität erfolgt. Das ist nicht sinnvoll, wenn man an der Bootlader Konsole arbeitet, aber man kann die Wartezeit verlängern: | |
<pre> | <pre> | ||
setenv boot_menu_timeout [seconds] | setenv boot_menu_timeout [seconds] | ||
</pre> | </pre> | ||
| − | + | Nachdem das Telefon eingeschaltet ist, gibt es eine kurze Zeit, in der Sie eine Verbindung auf die Konsole herstellen und das automatische Booten abbrechen können, ohne auf das Menü zu zugreifen. | |
<pre> | <pre> | ||
setenv bootdelay [seconds] | setenv bootdelay [seconds] | ||
</pre> | </pre> | ||
| − | ===== | + | ===== Ausschalten ===== |
| − | + | Nutzen Sie | |
neo1973 power-off | neo1973 power-off | ||
| − | + | um das Gerät vom Bootlader Prompt heraus auszuschalten | |
| − | ===== | + | ===== Ähnliche Akkuladegeräte ===== |
| − | + | Für eine detailierte Beschreibung der Ladegerät Spezifikation, lesen Sie [[Neo1973 Battery Charger]]. | |
| − | ====== | + | ====== Erkennen des Ladezustandes ====== |
| − | + | So können sie den Aktuellen Ladezustand abfragen: | |
neo1973 charger status | neo1973 charger status | ||
| − | + | Folgende Optionen sind möglich: | |
| − | + | ||
* idle - no charging | * idle - no charging | ||
* trickle - FIXME | * trickle - FIXME | ||
| Line 511: | Line 503: | ||
* fast_cccv - Fast (500mA) charging, using Constant-Current followed by Constant Voltage (Li-Ion) | * fast_cccv - Fast (500mA) charging, using Constant-Current followed by Constant Voltage (Li-Ion) | ||
| − | ====== | + | ====== Ausschalten des Ladevorganges ====== |
| − | + | Sie können das Laden der Batterie ausschalten (bis zum nächsten Neustart): | |
neo1973 charger off | neo1973 charger off | ||
| − | ====== | + | ====== Schnelle Aufladung erzwingen ====== |
| − | + | Geben Sie ein | |
neo1973 charger fast | neo1973 charger fast | ||
| − | + | um durch die PMU schnelles Laden (500mA) der Batterie zu erzwingen. Dies wird unterbrochen, falls die Batterie das Temperaturlimit erreicht oder andere Fehler auftreten. | |
| − | + | Folgende Kommandos erzeugen einen Bootmenü Eintrag, der auf das schnelle Laden umschalten und die Hintergrundbeleuchtung ausschaltet: | |
setenv menu_6 Fast-Charge and Backlight Off: neo1973 charger fast\; neo1973 backlight off | setenv menu_6 Fast-Charge and Backlight Off: neo1973 charger fast\; neo1973 backlight off | ||
saveenv | saveenv | ||
| − | + | In diesem Zustand kann das Neo1973 mit einem normalen USB Ladegerät aufgeladen werden. Sie müssen folgendes setzen | |
setenv boot_menu_timeout 65000 | setenv boot_menu_timeout 65000 | ||
saveenv | saveenv | ||
| − | + | um es vom Herunterfahren abzuhalten. | |
| − | ====== | + | ====== Einschalten / Ausschalten der automatischen Aufladung ====== |
| − | Autofast | + | Autofast ist eine Eigenschaft der PCF50606 PMU. Es bedeutet, dass der fast_cccv automatisch aktiviert wird, wenn ein Ladegerät mit geeigneter Spannung angeschlossen wird und die Batterie nicht über dem Temperaturlimit ist. |
| − | {{ | + | {{Warnung|Dies ist potenziell gefährlich. Nur Autofast aktivieren, wenn Sie SICHER sind, dass die 500mA am USB Anschluss anliegen. Dies ist der Fall mit einem Steckdosen Ladegerät, einem aktiven Hub oder einem Desktop-PC Hub. Bus powered Hubs und einige Laptops liefern nur 100mA auf ihren USB Ports und unterstützen somit kein schnelles Laden.}} |
| + | So Können Sie autofast ein- oder ausschalten: | ||
You can enable or disable autofast by | You can enable or disable autofast by | ||
neo1973 charger autofast | neo1973 charger autofast | ||
| − | + | respektiv | |
neo1973 charger !autofast | neo1973 charger !autofast | ||
| − | |||
| − | ===== | + | ===== Hintergrundbeleuchtung ===== |
| − | + | So können Sie die Hintergrundbeleuchtung ein- oder ausschalten: | |
neo1973 backlight on | neo1973 backlight on | ||
| − | + | respektiv | |
neo1973 backlight off | neo1973 backlight off | ||
| − | |||
===== Vibrator ===== | ===== Vibrator ===== | ||
| + | So können Sie den Vibrator ein- oder ausschalten: | ||
You can switch the vibrator on and off by using | You can switch the vibrator on and off by using | ||
neo1973 vibrator on | neo1973 vibrator on | ||
| − | + | respektiv | |
neo1973 vibrator off | neo1973 vibrator off | ||
| − | |||
===== GSM ===== | ===== GSM ===== | ||
| − | + | Seit der Patch Serie '''SVN revision 2885''' unterstützt u-boot den Zugriff auf das GSM Modem, und sogar den Zugriff darauf aus der Konsole heraus. | |
| − | + | ||
====== GSM power ====== | ====== GSM power ====== | ||
| − | + | So können sie den GSM ein- oder ausschalten: | |
neo1973 gsm on | neo1973 gsm on | ||
| − | + | respektiv | |
neo1973 gsm off | neo1973 gsm off | ||
| − | |||
| − | ====== | + | ====== Terminal Modus ====== |
| − | + | Sie können mit Hilfe eines im u-boot eingebauten Terminal Emulator auf den GSM Modem zugreifen. | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| + | Folgendes Beispiel demonstriert dies: | ||
<pre> | <pre> | ||
GTA01Bv4 # neo1973 gsm on | GTA01Bv4 # neo1973 gsm on | ||
| Line 603: | Line 591: | ||
</pre> | </pre> | ||
| − | + | Hinweis: Wenn Sie den Terminal Emulator ''cu'' auf Ihrem Host PC für den Zugriff auf u-boot nutzen, dann drücken Sie '~' um sicherzustellen, dass Sie auf dem Neo sind. | |
| − | + | ||
| − | ==== S3C2410 | + | ==== S3C2410 spezifische Kommandos ==== |
<pre> | <pre> | ||
| Line 625: | Line 612: | ||
</pre> | </pre> | ||
| − | ===== 266MHz | + | ===== 266MHz Taktfrequenz ===== |
| − | + | Sie können die [[S3C2410]] PLL neu konfigurieren, um eine Taktfrequenz von 266MHz (anstatt standard 200MHz) zu erreichen in dem Sie | |
GTA01Bv2 # s3c2410 speed set 266 | GTA01Bv2 # s3c2410 speed set 266 | ||
| − | + | bzw. | |
GTA01Bv2 # s3c2410 speed set 202 | GTA01Bv2 # s3c2410 speed set 202 | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | {{warning|Die ältere Hardware (Phase 0 - GTA01Bv3) läft nur mit 266MHz stabil, wenn Sie alles anschließen (spez. das FPC / [[Debug Board]] auf dem Debug Port}} | |
| − | + | ==== TFTP auf QT2410 ==== | |
| − | + | Das QT2410 cs8900a Ethernet kann genutzt werden um die Images per Netzwerk zu laden. | |
| + | Zuerst müssen Sie sicherstellen, dass ''ipaddr'', ''serverip'', ''ethaddr' und ''netmaskk''korrekt in Ihrer Umgebung eingerichtet sind: | ||
<pre> | <pre> | ||
QT2410 # printenv | QT2410 # printenv | ||
| Line 650: | Line 635: | ||
| − | ===== TFTP | + | ===== TFTP Kernel Download ===== |
<pre> | <pre> | ||
| Line 667: | Line 652: | ||
</pre> | </pre> | ||
| − | + | Sie können dann Booten über | |
<pre> | <pre> | ||
QT2410# bootm 0x32000000 | QT2410# bootm 0x32000000 | ||
| Line 674: | Line 659: | ||
== Device Firmware Upgrade == | == Device Firmware Upgrade == | ||
| − | + | Unsere Version von u-boot implementiert das [[USB DFU]]. Dies kann nützlich sein um schnell Dateien oder Kernel für einen Test zu laden. | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | Um herauszufinden, ob Ihre Version von u-boot dies unterstützt, nutzen Sie die Ausgabe von | |
$ lsusb -v -d 1457:5119 | $ lsusb -v -d 1457:5119 | ||
| − | + | solange sich das Telefon im u-boot Mudus befindet. | |
| − | + | Wenn es DFU unterstützt, sollten Sie folgenden Ausschnitt am Ende der Ausgabe sehen: | |
<pre> | <pre> | ||
Interface Descriptor: | Interface Descriptor: | ||
| Line 695: | Line 679: | ||
</pre> | </pre> | ||
| − | + | Um Informationen über Firmware Upgrade zu erhalten, lesen Sie [[dfu-util]]. | |
| − | === | + | === Dateien Booten über DFU === |
| − | + | Um eine Datei an die Speicheradresse 0x32000000 zu laden: | |
<pre> | <pre> | ||
dfu-util -a 0 -D fileToLoad -R | dfu-util -a 0 -D fileToLoad -R | ||
</pre> | </pre> | ||
| − | + | Danach senden Sie 'bootm 0x32000000' zum u-boot oder 'bootelf 0x32000000' wenn das eine ELF Binärdatei ist. | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| + | Simples Python Script, das eine ELF Image booten kann, vermeidet den ACM Bug in großen Paketen: | ||
<pre> | <pre> | ||
#!/usr/bin/python | #!/usr/bin/python | ||
| Line 744: | Line 726: | ||
</pre> | </pre> | ||
| − | == | + | == Fehlerbehebung == |
| − | === USB | + | === USB Verbindungsprobleme === |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| + | Ich bekam folgenden Fehler (in dmesg or /var/log/messages) auf der Host Seite beim Verbinden des Neo zu u-boot: | ||
usb 2-1: device descriptor read/64, error -110 | usb 2-1: device descriptor read/64, error -110 | ||
usb usb2: Controller not stopped yet! | usb usb2: Controller not stopped yet! | ||
| − | + | Das Problem verschwindet zumindest auf Hostseite durch unten genannten Befehl. Bitte beachten Sie, dass es möglicherweise zu Problemen führen kann, falls Sie USB Tastatur/Maus haben. Der Autor konnte dies in Ermangelung der Geräte nicht testen. | |
| − | + | ||
rmmod uhci_hcd ; modprobe uhci_hcd | rmmod uhci_hcd ; modprobe uhci_hcd | ||
| − | + | [[Category:System Developers/de]] | |
| − | + | ||
| − | [[Category: | + | |
| − | + | ||
Latest revision as of 15:34, 1 February 2010
| Languages: |
English • العربية • Български • Česky • Dansk • Deutsch • Esperanto • Eesti • Español • فارسی • Suomi • Français • עברית • Magyar • Italiano • 한국어 • Nederlands • Norsk (bokmål) • Polski • Português • Română • Русский • Svenska • Slovenčina • Українська • 中文(中国大陆) • 中文(台灣) • Euskara • Català |
[edit] Phase0 Schnellstart
- Überprüfen, dass die Batterie eingebaut ist und das USB Kabel innerhalb der letzten 30 Sekunden nirgendwo angeschlossen war.
- Das Neo (nicht das Debug Board) an einen Linux Rechner mit dem USB Kabel anschließen.
- Gleichzeitig die AUX und Power-up gedrückt halten, um ins Bootmenü zu gelangen.
- Die Konsole auf USB einstellen.
- Am /dev/ttyACM0 mit einem Terminalprogramm über einen Linux Rechner (evtl. "chown uucp.uucp /dev/ttyACM0" notwendig) verbinden.
- Beachten Sie, dass der cdc_acm /dev/ttyACM0 Zugang wärend des Ladevorganges nicht verfügbar ist, und im weiteren funktioniert der Zugriff über die Netzwerkschnittstelle usb0.
- Jetzt sehen sie das Bootlader Menü.
[edit] Allgemein
Das GTA01 nutzt den u-boot Bootlader.
Mehr Informationen zu u-boot finden Sie unter
- http://www.denx.de/wiki/DULG
- http://www.gumstix.org/tikiwiki/tiki-index.php?page=U-Boot
- http://linuxdevices.com/articles/AT5085702347.html
Bereits implementierte Erweiterungen zum Vanilla u-boot enthalten:
- Unterstützung für das Booten vom NAND Flash unter Verwendung von S3C2410 Steppingstone
- Unterstützung des S3C2410 NAND Flash
- Unterstützung für das Downloaden von Programmen über den S3C2410 USB Device Controller
- Unterstützung der Fortschrittsanzeige bzw. des Logos über den S3C2410 Framebuffer beim Booten
Jedoch unterstützt u-boot einige für das GTA01 erforderliche Funktionen nicht:
- Unterstützung für das Laden des Kernels/initrd von der SD/Transflash Karte
User:HaraldWelte is working on those issues, and in fact most of them have already been implemented.
[edit] Bootlader Quellcode
Die aktuellen Patches des Bootladers sind zu finden unter http://svn.openmoko.org/trunk/src/target/u-boot/patches/.
Entpacken Sie die Quellen, wenden Sie den Patch an, führen Sie "make gta01bv3_config" (oder "gta01bv2_config" bzw. die entsprechende Hardwareversion) aus und führen Sie "make" aus. Als Resultat erhalten sie die Binärdatei "u-boot.bin", welche Sie direkt (entweder mit dem vorhandenen Bootlader oder sjf2410-linux) in den NAND Flash Speicher laden können.
[edit] Bootlader Binärdatei
Das aktuellste Binärimage des Bootladers finden Sie unter http://downloads.openmoko.org/daily/ . Dieses sollte auf die Adresse 0x00000000 im NAND Flashspeichers geschrieben werden (Größe 0x30000).
[edit] Bootloader Entwicklung
[edit] QT2410
Wenn Sie de Entwicklung des Bootladers unter QT2410 betreiben möchten, dann ist es einfacher, mit einem Bootlader Image zu arbeiten, das per USB ins Ram geflasht werden kann.
Um dies zu tun, müssen Sie die Datei u-boot/include/configs/qt2410.h editieren ("if 0" in der Zeile 32 auf "if 1" ändern) und danach mit "make" neu übersetzen.
Die resultierende Datei "u-boot.bin" ist _NICHT_ für NAND verwendbar, sondern nur direkt im RAM, indem Sie z.B. das Programm s3c2410_boot_usb verwenden.
[edit] GTA01
Bootlader Entwicklung unter GTA01 ist etwas trickreich. Zuerst gibt es keinen NOR Flash. Weiterhin gibt es aber keine andere Weise vom NAND zu laden. Folglich haben wir keinen USB Downloader wie das QT2410.
Das Hauptproblem ist: Das S3C2410 Steppingstone kopiert unbedingt die ersten 4k des Flashes ins interne SRAM. Das SRAM Segment bleibt an der physischen Adresse allerdings auf null.
[edit] Nutzen des JTAG zum Booten aus dem RAM
So, wie kann man nun vom RAM booten? Dazu nutzt man JTAG / OpenOCD, um
- Zurücksetzen und Halten der CPU auf PC=0
> reset halt target halted in ARM state due to debug request, current mode: Supervisor cpsr: 0x400000d3 pc: 0x00000000 MMU: disabled, D-Cache: disabled, I-Cache: disabled
- Herunterladen eines kleinen Stückes Code vom SRAM (4k SRAM von Steppingstone überschreiben).
> load_binary /space/misc/gta01/u-boot.git/board/gta01/lowlevel_foo.bin 0 downloaded 332 byte in 0s 21899us
- Setzen einer Sprungmarke an der Adresse 0x33f80000 (was anzeigt, dass das low-level Code an dieser Stelle endet)
> bp 0x33f80000 4 hw breakpoint added at address 0x33f80000
- Den Code bis zur Sprungmarke ausführen
> resume Target 0 resumed > Target 0 halted target halted in ARM state due to breakpoint, current mode: Supervisor cpsr: 0x600000d3 pc: 0x33f80000 MMU: disabled, D-Cache: disabled, I-Cache: enabled
- Das u-boot Image auf die Ardesse 0x33f80000 laden
> load_binary /space/misc/gta01/u-boot.git/u-boot.bin 0x33f80000 downloaded 135692 byte in 6s 567264us
- Ausführung fortsetzen
> resume Target 0 resumed
Ab diesem Punkt wird die Hintergrundbeleuchtung hell und man sieht folgende vertraute Kommandozeilenaufforderung auf der seriellen Konsole.
U-Boot 1.1.6 (Jan 13 2007 - 23:44:23) DRAM: 128 MB NAND: 64 MiB *** Warning - bad CRC or NAND, using default environment In: serial Out: serial Err: serial Hit any key to stop autoboot: 0 GTA01Bv2 #
[edit] Erzeugen der bootbaren Images
u-boot benötigt bootbare Images (wie der Kernel, aber auch initrd und andere) in Form des sogenannten uImage. Um ein uImage von z.B. einem vmlinuz zu erzeugen, kann man wie folgt vorgehen:
objcopy -O binary -R .note -R .comment -S vmlinux linux.bin
gzip -9 linux.bin
u-boot/tools/mkimage -A arm -O linux -T kernel -C gzip -a 30008000 -e 30008000 \
-n "Kernel Image QT2410" -d linux.bin.gz uImage
[edit] Bootmenü
Ab dem Phase-0 Release zeigt jetzt unsere u-boot Version ein Bootmenü auf dem Startbildschirm an.
[edit] Zugriff auf das Bootmenü
Um ins Bootmenü zu gelangen, müssen Sie gleichzeitig den Neo1973 AUX Button und den Power Button gedrückt halten.
[edit] Nutzung des Bootmenü
Mit dem Neo1973 AUX Button können Sie zwischen den Menüoptionen wechseln. Mit dem POWER Button wählen Sie eine Option aus.
[edit] Hunzufügen von Menüpunkten zum Bootmenü
Sie können weitere Optionen zum Bootmenü hinzufügen indem Sie Umgebungsvariablen setzen. Die kanonische Form ist menu_<number> <Title>: U-Boot-Commands
Zum Beispiel fügt folgender Befehl einen Menüeintrag, der auf das Schnellladen schaltet und die Hintergrundbeleuchtung deaktiviert:
setenv menu_6 Autofast-Charge and Backlight Off: neo1973 charger autofast\; neo1973 backlight off saveenv
In diesem Zustand kann das Neo1973 mit einem üblichen USB Ladegerät aufgeladen werden. Sie müssen allerdings 'setenv boot_menu_timeout 65000' setzen, um das Abschalten zu verhindern.
[edit] Bootlader Kommandozeile
[edit] Zugriff auf den Bootlader Prompt
Der Bootlader Prompt steht entweder auf einer seriellen Konsole (über Debug Board) oder als virtuelles serielle USB Gerät (USB CDC_ACM) zur Verfügung. Ob serielle Schnittstelle oder USB Port verwendet werden, hängt von den u-boot Umgebungsvariablen stdin, stdout und stderr ab.
Unabhängig davon, ob Sie usbtty nutzen oder nicht, die ersten Nachrichten werden immer auf der seriellen Konsole angezeigt.
Der Bootlader ist so konfiguriert, dass er drei Sekunden wartet. Wenn innerhalb dieser drei Sekunden eine Taste auf stdin gedrückt wird, wird der automatische Bootvorgang abgebrochen.
[edit] Nutzung von usbtty unter Linux
Durch den Anschluss des Neo im u-boot Modus am PC, sollte ein CDC ACM Gerät erkannt werden und Sie können ihn über /dev/ttyACM0 ansprechen. Wenn nicht, aktivieren Sie die CONFIG_USB_ACM Unterstützung (Device Drivers -> USB support -> USB Modem (CDC ACM) support). Anleitungen für MaxOS X User befinden sich hier.
Für den Zugriff verwenden Sie Ihren bevorzugten Terminalemulator (minicom, cu, zc, screen ...) wie auf jede andere serielle Schnittstelle. Wenn Sie keinen Favoriten haben, versuchen Sie es einfach:
cu -l /dev/ttyACM0
Eventuell ist folgender Befehl notwendig:
chown uucp.uucp /dev/ttyACM0
um die erforderlichen Rechte zu erhalten (auch als root).
Zuerst sollten Sie prüfen, ob das USB Gerät wärend des u-boot Modus in 'lsusb' angezeigt wird:
# lsusb -d 1457:5119 Bus 005 Device 079: ID 1457:5119
Als zweites können weitere Informationen über das Endgerät und deren Konfiguration angezeigt werden:
# lsusb -v -d 1457:5119
Bus 005 Device 079: ID 1457:5119
Device Descriptor:
bLength 18
bDescriptorType 1
bcdUSB 1.10
bDeviceClass 2 Communications
bDeviceSubClass 0
bDeviceProtocol 0
bMaxPacketSize0 16
idVendor 0x1457
idProduct 0x5119
bcdDevice 0.00
iManufacturer 1 Openmoko, Inc
iProduct 2 Neo1973 Bootloader U-Boot 1.2.0-g6c7cac8c-dirty-moko3
iSerial 3 0000000
bNumConfigurations 1
Configuration Descriptor:
bLength 9
bDescriptorType 2
wTotalLength 85
bNumInterfaces 3
bConfigurationValue 1
iConfiguration 4 TTY via USB
bmAttributes 0xc0
Self Powered
MaxPower 0mA
Interface Descriptor:
bLength 9
bDescriptorType 4
bInterfaceNumber 0
bAlternateSetting 0
bNumEndpoints 1
bInterfaceClass 2 Communications
bInterfaceSubClass 2 Abstract (modem)
bInterfaceProtocol 1 AT-commands (v.25ter)
iInterface 6 Control Interface
CDC Header:
bcdCDC 0.6e
CDC Call Management:
bmCapabilities 0x00
bDataInterface 1
CDC ACM:
bmCapabilities 0x00
CDC Union:
bMasterInterface 0
bSlaveInterface 1
Endpoint Descriptor:
bLength 7
bDescriptorType 5
bEndpointAddress 0x81 EP 1 IN
bmAttributes 3
Transfer Type Interrupt
Synch Type None
Usage Type Data
wMaxPacketSize 0x0010 1x 16 bytes
bInterval 255
Interface Descriptor:
bLength 9
bDescriptorType 4
bInterfaceNumber 1
bAlternateSetting 0
bNumEndpoints 2
bInterfaceClass 10 CDC Data
bInterfaceSubClass 0 Unused
bInterfaceProtocol 0
iInterface 5 Bulk Data Interface
Endpoint Descriptor:
bLength 7
bDescriptorType 5
bEndpointAddress 0x02 EP 2 OUT
bmAttributes 2
Transfer Type Bulk
Synch Type None
Usage Type Data
wMaxPacketSize 0x0010 1x 16 bytes
bInterval 255
Endpoint Descriptor:
bLength 7
bDescriptorType 5
bEndpointAddress 0x83 EP 3 IN
bmAttributes 2
Transfer Type Bulk
Synch Type None
Usage Type Data
wMaxPacketSize 0x0010 1x 16 bytes
bInterval 255
Interface Descriptor:
bLength 9
bDescriptorType 4
bInterfaceNumber 2
bAlternateSetting 0
bNumEndpoints 0
bInterfaceClass 254 Application Specific Interface
bInterfaceSubClass 1 Device Firmware Update
bInterfaceProtocol 1
iInterface 7 USB Device Firmware Upgrade
Device Status: 0x0001
Self Powered
Als nächstes können Sie es mit einem beliebigen Terminal Programm nutzen.
Wenn die Umgebung nicht richtig gesetzt ist, dann müssen Sie die aktuelle Konsole nutzen (z.B. serielle Konsole) um sie zu setzen:
GTA01Bv2 # setenv stderr usbtty GTA01Bv2 # setenv stdout usbtty GTA01Bv2 # setenv stdin usbtty
[edit] Typischer u-boot Prompt
U-Boot 1.2.0-moko1 (Feb 16 2007 - 00:36:13) DRAM: 128 MB NAND: 64 MiB Found Environment offset in OOB.. Video: 640x480x8 31kHz 59Hz USB: S3C2410 USB Deviced In: serial Out: serial Err: serial Hit any key to stop autoboot: 0 GTA01Bv3 #
[edit] Kommandos auf dem Bootlader Prompt
[edit] Auto-boot
Auto-boot führt in der Umgebungsvariable bootcmd definierte Kommandos aus. Standard Konfiguration ist:
GTA01Bv3 # printenv
bootcmd=setenv bootargs ${bootargs_base} ${mtdparts}; nand read.e 0x32000000 kernel; bootm 0x32000000
Dies bedeutet, dass es versucht wird zuerst die NAND Partition kernel in die Speicheradresse 0x32000000 zu kopieren und und sie dann zu starten.
[edit] Umgebung
u-boot ist konfiguriert, um die Umgebung im nichtflüchtigen NAND Flash Speicher zu verwalten. Sie können folgende Kommandos nutzen, um die Umgebung zu lesen, verändern oder zu speichern:
GTA01Bv2 # printenv
baudrate=115200
bootargs=rootfstype=jffs2 root=/dev/mtdblock4 console=ttySAC0,115200 console=tty0 loglevel=8 dyntick=enable lpj=252416
usbtty=cdc_acm
bootdelay=10
stdout=serial
stderr=serial
stdin=serial
mtdparts=mtdparts=neo1973-nand:0x00030000(u-boot),0x0000c000(u-boot_env),0x00200000(kernel),0x00130000(splash),0x03c94000(rootfs)
mtdids=nand0=neo1973-nand
bootargs_base=rootfstype=jffs2 root=/dev/mtdblock4 console=ttySAC0,115200 console=tty0 loglevel=8 dyntick=enable lpj=252416
bootcmd=setenv bootargs ${bootargs_base} ${mtdparts}; nand read.e 0x32000000 kernel; bootm 0x32000000
pcf50606_int1=0x40
filesize=160C000
partition=nand0,0
mtddevnum=0
mtddevname=u-boot
Environment size: 670/16380 bytes
GTA01Bv3 # setenv bootdelay 10
GTA01Bv3 # printenv bootdelay
bootdelay=10
GTA01Bv3 # saveenv
Saving Environment to NAND...
Erasing Nand...Writing to Nand... done
GTA01Bv3 #
Hinweis: Wenn mehrere Kommandos gesetzt sind, z.B. für bootcmd, dann sind Trennzeichen ';' notwendig, zum Beispiel
GTA01Bv3 # setenv bootcmd mmcinit\; ext2load mmc 0 0x32000000 uImage\; bootm 0x32000000
[edit] MMC/SD
Zur Initialisierung einer MMC/SD Karte, müssen Sie das Kommando mmcinit nutzen:
GTA01Bv3 # mmcinit trying to detect SD Card... MMC found. Card desciption is: Manufacturer ID = 58d564 HW/FW Revision = 3 8 Product Name = 21DN!@X� Serial Number = 445303 Month = 5 Year = 2000 READ_BL_LEN=15, C_SIZE_MULT=7, C_SIZE=3197 size = 4208984064 GTA01Bv3 #
Danach kann ein ext2 Dateisystem gelesen werden:
GTA01Bv3 # ext2ls mmc 0
<DIR> 1024 .
<DIR> 1024 ..
<DIR> 12288 lost+found
1544788 uImage
[edit] NAND
GTA01Bv3 # help nand
nand info - show available NAND devices
nand device [dev] - show or set current device
nand read[.jffs2] - addr off size
nand write[.jffs2] - addr off size - read/write `size' bytes starting
at offset `off' to/from memory address `addr'
nand erase [clean] [off size] - erase `size' bytes from
offset `off' (entire device if not specified)
nand bad - show bad blocks
nand dump[.oob] off - dump page
nand scrub - really clean NAND erasing bad blocks (UNSAFE)
nand markbad off - mark bad block at offset (UNSAFE)
nand biterr off - make a bit error at offset (UNSAFE)
[edit] Laden des Kernels aus dem NAND
GTA01Bv3 # nand read 0x32000000 kernel NAND read: device 0 offset 212992, size 2097152 ... 2097152 bytes read: OK GTA01Bv3 # bootm 0x32000000 ## Booting image at 32000000 ... Image Name: Openmoko Kernel Image Neo1973 Created: 2007-02-15 23:54:18 UTC Image Type: ARM Linux Kernel Image (gzip compressed) Data Size: 1546258 Bytes = 1.5 MB Load Address: 30008000 Entry Point: 30008000 Verifying Checksum ... OK Uncompressing Kernel Image ... OK Starting kernel ...
[edit] Neuen Bootlader ins NAND schreiben
Folgende Kommandofolge lädt die Datei u-boot.bin aus dem ext2/mms und flasht diese in die Bootlader Flash Partition:
GTA01Bv3 # ext2load mmc 0 0x32000000 u-boot.bin
GTA01Bv3 # nand erase u-boot
GTA01Bv3 # nand write.e 0x32000000 u-boot ${filesize}
[edit] Neuen Kernel ins NAND schreiben
Folgende Kommandofolge lädt die Datei uImage aus dem ext2/mmc und flasht sie in die Kernel Flash Partition:
GTA01Bv3 # ext2load mmc 0 0x32000000 uImage
GTA01Bv3 # nand erase kernel
GTA01Bv3 # nand write.e 0x32000000 kernel ${filesize}
[edit] Neues Hauptdateisystem (rootfs) ins NAND schreiben
Folgende Kommandofolge lädt die Datei rootfs.jffs2 aus dem ext2/mmc und flasht sie in die rootfs Flash Partition:
GTA01Bv3 # ext2load mmc 0 0x32000000 rootfs.jffs2
GTA01Bv3 # nand erase rootfs
GTA01Bv3 # nand write.e 0x32000000 rootfs ${filesize}
Bitte beachten Sie, dass dies nur mit root-Dateisystem Größen funktioniert, die kleiner sind als die Größe des Speichers vor 0x32000000, der im Falle von 64MB SDRAM ungefähr 32MB groß ist.
[edit] Unter Neo1973 verfügbare Kommandos
Unsere Version von u-boot unterstützt eine Reihe von Neo1973 spezifischen Befehle:
GTA01Bv2 # help neo1973 neo1973 neo1973 info - display phone informantion neo1973 power-off - switch off the phone neo1973 charger status - display charger status neo1973 charger autofast - enable automatic fast (500mA) charging neo1973 charger !autofast - disable automatic fast (500mA) charging neo1973 charger fast - enable fast (500mA) charging neo1973 charger off - disable charging neo1973 backlight (on|off) - switch backlight on or off neo1973 vibrator (on|off) - switch vibrator on or off neo1973 udc pullup (on|off) - switch pull-up on or off
Was ist das udc?
[edit] Timeouts
Wenn das Bootlader Menü angezeigt wird, wird das Telefon ausgeschaltet, falls eine Weile keine Aktivität erfolgt. Das ist nicht sinnvoll, wenn man an der Bootlader Konsole arbeitet, aber man kann die Wartezeit verlängern:
setenv boot_menu_timeout [seconds]
Nachdem das Telefon eingeschaltet ist, gibt es eine kurze Zeit, in der Sie eine Verbindung auf die Konsole herstellen und das automatische Booten abbrechen können, ohne auf das Menü zu zugreifen.
setenv bootdelay [seconds]
[edit] Ausschalten
Nutzen Sie
neo1973 power-off
um das Gerät vom Bootlader Prompt heraus auszuschalten
[edit] Ähnliche Akkuladegeräte
Für eine detailierte Beschreibung der Ladegerät Spezifikation, lesen Sie Neo1973 Battery Charger.
[edit] Erkennen des Ladezustandes
So können sie den Aktuellen Ladezustand abfragen:
neo1973 charger status
Folgende Optionen sind möglich:
- idle - no charging
- trickle - FIXME
- pre - Slow (100mA) charging, works in hardware.
- fast_cccv - Fast (500mA) charging, using Constant-Current followed by Constant Voltage (Li-Ion)
[edit] Ausschalten des Ladevorganges
Sie können das Laden der Batterie ausschalten (bis zum nächsten Neustart):
neo1973 charger off
[edit] Schnelle Aufladung erzwingen
Geben Sie ein
neo1973 charger fast
um durch die PMU schnelles Laden (500mA) der Batterie zu erzwingen. Dies wird unterbrochen, falls die Batterie das Temperaturlimit erreicht oder andere Fehler auftreten.
Folgende Kommandos erzeugen einen Bootmenü Eintrag, der auf das schnelle Laden umschalten und die Hintergrundbeleuchtung ausschaltet:
setenv menu_6 Fast-Charge and Backlight Off: neo1973 charger fast\; neo1973 backlight off saveenv
In diesem Zustand kann das Neo1973 mit einem normalen USB Ladegerät aufgeladen werden. Sie müssen folgendes setzen
setenv boot_menu_timeout 65000 saveenv
um es vom Herunterfahren abzuhalten.
[edit] Einschalten / Ausschalten der automatischen Aufladung
Autofast ist eine Eigenschaft der PCF50606 PMU. Es bedeutet, dass der fast_cccv automatisch aktiviert wird, wenn ein Ladegerät mit geeigneter Spannung angeschlossen wird und die Batterie nicht über dem Temperaturlimit ist.
| WARNUNG: Dies ist potenziell gefährlich. Nur Autofast aktivieren, wenn Sie SICHER sind, dass die 500mA am USB Anschluss anliegen. Dies ist der Fall mit einem Steckdosen Ladegerät, einem aktiven Hub oder einem Desktop-PC Hub. Bus powered Hubs und einige Laptops liefern nur 100mA auf ihren USB Ports und unterstützen somit kein schnelles Laden. |
So Können Sie autofast ein- oder ausschalten: You can enable or disable autofast by
neo1973 charger autofast
respektiv
neo1973 charger !autofast
[edit] Hintergrundbeleuchtung
So können Sie die Hintergrundbeleuchtung ein- oder ausschalten:
neo1973 backlight on
respektiv
neo1973 backlight off
[edit] Vibrator
So können Sie den Vibrator ein- oder ausschalten: You can switch the vibrator on and off by using
neo1973 vibrator on
respektiv
neo1973 vibrator off
[edit] GSM
Seit der Patch Serie SVN revision 2885 unterstützt u-boot den Zugriff auf das GSM Modem, und sogar den Zugriff darauf aus der Konsole heraus.
[edit] GSM power
So können sie den GSM ein- oder ausschalten:
neo1973 gsm on
respektiv
neo1973 gsm off
[edit] Terminal Modus
Sie können mit Hilfe eines im u-boot eingebauten Terminal Emulator auf den GSM Modem zugreifen.
Folgendes Beispiel demonstriert dies:
GTA01Bv4 # neo1973 gsm on GTA01Bv4 # terminal serial switching s3ser0 from console into GSM mode Entering terminal mode for port serial Use '~.' to leave the terminal and get back to u-boot ATE1 OK AT+CGMI? ERROR AT+CGMI FIC OK AT+CGMR GTA01Bv4 OK ~[u-boot]~. switched s3ser0 from GSM mode back into console mode GTA01Bv4 # neo1973 gsm off GTA01Bv4 #
Hinweis: Wenn Sie den Terminal Emulator cu auf Ihrem Host PC für den Zugriff auf u-boot nutzen, dann drücken Sie '~' um sicherzustellen, dass Sie auf dem Neo sind.
[edit] S3C2410 spezifische Kommandos
GTA01Bv2 # help s3c2410 s3c2410 speed get - display current PLL speed config s3c2410 speed list - display supporte PLL speed configs s3c2410 speed set - set PLL speed GTA01Bv2 # s3c2410 speed list 50 MHz 101 MHz 202 MHz 266 MHz GTA01Bv2 # s3c2410 speed get FCLK = 202 MHz, HCLK = 101 MHz, PCLK = 50 MHz GTA01Bv2 # s3c2410 speed set 101 GTA01Bv2 # s3c2410 speed get FCLK = 101 MHz, HCLK = 50 MHz, PCLK = 50 MHz
[edit] 266MHz Taktfrequenz
Sie können die S3C2410 PLL neu konfigurieren, um eine Taktfrequenz von 266MHz (anstatt standard 200MHz) zu erreichen in dem Sie
GTA01Bv2 # s3c2410 speed set 266
bzw.
GTA01Bv2 # s3c2410 speed set 202
| WARNING: Die ältere Hardware (Phase 0 - GTA01Bv3) läft nur mit 266MHz stabil, wenn Sie alles anschließen (spez. das FPC / Debug Board auf dem Debug Port |
[edit] TFTP auf QT2410
Das QT2410 cs8900a Ethernet kann genutzt werden um die Images per Netzwerk zu laden.
Zuerst müssen Sie sicherstellen, dass ipaddr, serverip, ethaddr' und netmaskkkorrekt in Ihrer Umgebung eingerichtet sind:
QT2410 # printenv ethaddr=00:01:02:03:04:05 netmask=255.255.255.0 ipaddr=192.168.100.100 serverip=192.168.100.1
[edit] TFTP Kernel Download
QT2410 # tftpboot 0x32000000
*** Warning: no boot file name; using 'C0A86464.img'
TFTP from server 192.168.100.1; our IP address is 192.168.100.100
Filename 'C0A86464.img'.
Load address: 0x32000000
Loading: #################################################################
#################################################################
#################################################################
#################################################################
##########################################
done
Bytes transferred = 1544788 (179254 hex)
Sie können dann Booten über
QT2410# bootm 0x32000000
[edit] Device Firmware Upgrade
Unsere Version von u-boot implementiert das USB DFU. Dies kann nützlich sein um schnell Dateien oder Kernel für einen Test zu laden.
Um herauszufinden, ob Ihre Version von u-boot dies unterstützt, nutzen Sie die Ausgabe von
$ lsusb -v -d 1457:5119
solange sich das Telefon im u-boot Mudus befindet.
Wenn es DFU unterstützt, sollten Sie folgenden Ausschnitt am Ende der Ausgabe sehen:
Interface Descriptor:
bLength 9
bDescriptorType 4
bInterfaceNumber 2
bAlternateSetting 0
bNumEndpoints 0
bInterfaceClass 254 Application Specific Interface
bInterfaceSubClass 1 Device Firmware Update
bInterfaceProtocol 1
iInterface 0
Um Informationen über Firmware Upgrade zu erhalten, lesen Sie dfu-util.
[edit] Dateien Booten über DFU
Um eine Datei an die Speicheradresse 0x32000000 zu laden:
dfu-util -a 0 -D fileToLoad -R
Danach senden Sie 'bootm 0x32000000' zum u-boot oder 'bootelf 0x32000000' wenn das eine ELF Binärdatei ist.
Simples Python Script, das eine ELF Image booten kann, vermeidet den ACM Bug in großen Paketen:
#!/usr/bin/python
import sys
import os
import time
cmd1 = "neo backlight off\n"
cmd2 = "bootelf 0x32000000\n"
def output(tty, str):
for x in str:
tty.write(x)
tty.flush()
if len(sys.argv) == 2:
print "Loading %s..." % sys.argv[1]
loadfile = "dfu-util -a 0 -D %s -R" % sys.argv[1]
os.system(loadfile)
time.sleep(3)
tty = open("/dev/ttyACM0", "a")
output(tty, cmd1)
output(tty, cmd2)
tty.close()
else:
print "Usage: %s elffile" % sys.argv[0]
print ""
sys.exit(2)
[edit] Fehlerbehebung
[edit] USB Verbindungsprobleme
Ich bekam folgenden Fehler (in dmesg or /var/log/messages) auf der Host Seite beim Verbinden des Neo zu u-boot:
usb 2-1: device descriptor read/64, error -110 usb usb2: Controller not stopped yet!
Das Problem verschwindet zumindest auf Hostseite durch unten genannten Befehl. Bitte beachten Sie, dass es möglicherweise zu Problemen führen kann, falls Sie USB Tastatur/Maus haben. Der Autor konnte dies in Ermangelung der Geräte nicht testen.
rmmod uhci_hcd ; modprobe uhci_hcd