View source for Neo 1973 audio subsystem
From Openmoko
You do not have permission to edit this page, for the following reasons:
You can view and copy the source of this page:
Return to Neo 1973 audio subsystem.
You do not have permission to edit this page, for the following reasons:
You can view and copy the source of this page:
Return to Neo 1973 audio subsystem.
In the center of the Neo1973 audio subsystem is the WM8753 (the "Wolfson Codec"), which implements record (ADCs), playback (DACs), and signal mixing. On the stereo output is the LM4857 amplifier, which drives the stereo speakers, the mono earpiece and the headphones. Sound from and to GSM is received from and sent to the GSM modem via analog connections. There's a digital mono interface for sound from and to the Bluetooth chip.
The channel numbers shown here are for the Freerunner, not the 1973.
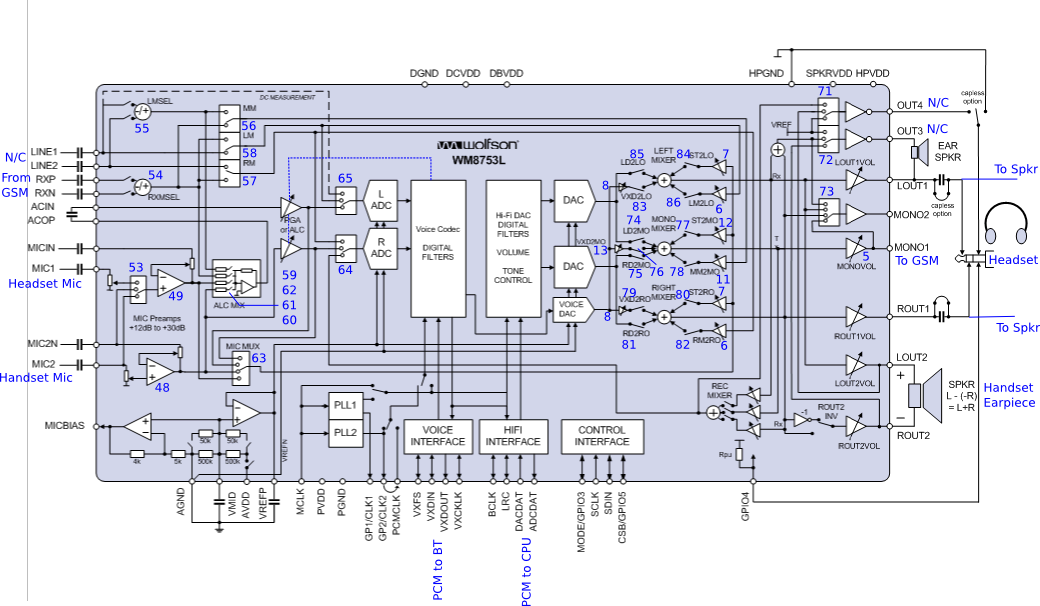 A way more pretty diagram is here
A way more pretty diagram is here
Png version with ALSA control names printed over (these are alsa controls like found in statefiles or amixer commands, alsamixer removes trailing "Playback Volume" and such where it sees fit) Inkscape source:
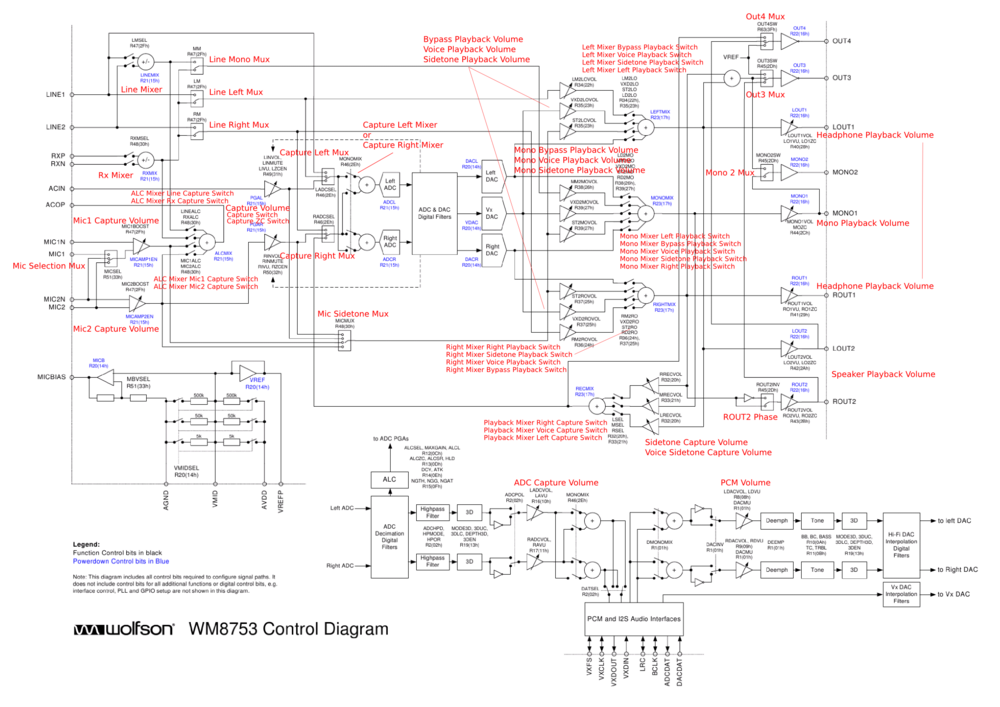
Four variants of using available Digital Audio Interfaces and DACs/ADC, these correspond to the "DAI Mode" ALSA control values:
Keep in mind: left interface (VXxxx) is connected to BlueTooth, right interface (LRC, BCLK, xxxDAT) is connected to SoC (CPU). So mode "11" at least seems isn't useful at all for the way Neo HW is built. Mode "10" is suited for (Stereo/mono) output and recording for digital world, whereas Mode "00" is needed for GSM<->BT operation (calls via BT-headset) only.
BT-VoIP-calls and BT-stereo-headphones playback are done via direct USB-connection SoC<->BT in a very usual standard-linux-way, and therefor need no statefile or any other setup of mixer.
We are still wondering what use Mode "01" might have, other than analog mixed mono output (which could as well be done at digital side by feeding L/R with same data)
In my experience this works but I have to fiddle with the connection a bit before I get stereo output. The audio also comes out both the speaker and headphones.
alsactl -f /etc/stereoout.state restore madplay myfavoritesong.mp3
Another simple test (assuming you have USB Networking configured) is to listen to a radio stream:
wget -O - http://radioparadise.steadyhost.com:8050 | madplay -
If for some reason you're missing stereoout.state, try getting a similar copy (a couple of volume levels are different is all)
wget http://opensource.wolfsonmicro.com/~gg/neo1973/stereoout.state
This is the default case.
Neo Mode is GSM Handset Amp Mode is Call Speaker
This should be supported by ASoC 0.13rc3 (-moko7 kernel) on.
ASoC 0.13.3 should have same functionality but has renamed the soundcard to neo1973.
https://people.openmoko.org/laforge/gta01/gta01b_v2/alsa/gsmhandset.state
For ASoC 0.13.3 http://opensource.wolfsonmicro.com/~gg/neo1973/gsmhandset.state
This is also a quite common case, since we ship the headset with the phone
Headset Detection is done via GPIO on S3C2410
Neo Mode is GSM Headset Amp Mode is Headphones
Supported in ASoC 0.13.3
http://opensource.wolfsonmicro.com/~gg/neo1973/gsmheadset.state
NOTE none of this works with GTA02. Neo mode has disappeared, and none of the state files are GTA02 compatible.
Headset detection via software
Neo Mode is GSM Bluetooth Amp Mode is Off
Should be support by ASoC 0.13.3
Example of how to setup PCM->BT link.
http://opensource.wolfsonmicro.com/~gg/bluetooth-pcm/bluetooth_pcm.c
http://opensource.wolfsonmicro.com/~gg/neo1973/gsmbluetooth.state
NOTE this will not work with GTA02, as the control numbers have changed Here [1] is a modified version that is GTA02 compatible, But lacks the Neo Mode settings which disappeared on GTA02, and does not seem to work.
The state file above does not work for me. I created one gsm_headset.txt that is working for audio playback on the freerunner. I will be updating that file as I get the mic routing working.
To use this state file there are a number of steps
Turn on bluetooth
Pair the headset ( this only needs to be done once ).
Start the audio subsystem and connect the headset http://wiki.bluez.org/wiki/HOWTO/AudioDevices or use my script BtHeadset.py
If you don't hear static in your headset at this point you may need to reboot.
Start the phone call
alsactl restore 0 -f gsm_headset.txt
I wrote a script to stop the headset too BtHeadsetDetach.py
The above did not work for me; for some reason, the hifi DAC interface must be exercised once before playing. I have hacked BtHeadset.py to make FR-BTAudio. When paired with GSMBLUETOOTH.txt I get 2-way high quality audio.
I did a lot of this debugging using w8753_dump which is a quick and dirty hack, but quite useful on a large text window.
For example, using a voip app on the phone with a bt voice headset. This would also be a good way to work on the bluetooth driver without requiring a working GSM and placing a lot of calls.
See ticket 583 for a state file that should route system audio *out* to the headset. The codec does not allow for duplex system audio connected to a headset, so audio in is still using the mic.
NOTE the state file specified does not work for GTA02, and even when modified to be GTA02 compatible still does not route system sound to a BT headset. Modified state file for GTA02 is here [2]
This is an important mode since it is also required for ringtone playback
This is working since ASoC 0.13rc2 (-moko6 kernel)
This should also work on ASoC 0.13.3
https://people.openmoko.org/laforge/gta01/gta01b_v2/alsa/stereoout.state
For ASoC 0.13.3 http://opensource.wolfsonmicro.com/~gg/neo1973/stereoout.state
This is working since ASoC 0.13rc2 (-moko6 kernel)
One way to do this is to use a pulse plugin for bluetooth audio. Pulse would be routed either to the plugin or the default route to the codec. The plugin would watch for headset connect/disconnect events generated by a bluez audio daemon to keep the list of available output devices current.
There is early work on the bluez daemon to handle this. It has been combined with an alsa plugin in the bluez tree but the alsa plugin probably will not be sufficient for neo.
This is mainly used to record notes
UNKNOWN
http://wiki.openmoko.org/wiki/User:Herp
http://wildsau.enemy.org/~moko/voice-recording.state
This is a nice wishlist item. The user should be able to receive the full-duplex audio from the wolfson codec, and record it using the S3C2410 IIS.
It is possible to do PCM recording of a GSM voice call. In fact, it is even possible to record the local microphone (what you speak) and the remote voice (what is spoken on the other end of the call) to separate channels (L and R of the Stereo ADC).
If you want to record a GSM voice call, please adjust your mixer settings as follows
FIXME: test this. There's currently a ASoC kernel driver bug preventing audio capture from working at all.
UNKNOWN
If you want to play PCM audio into a GSM call (i.e. make your remote partner of a voice call hear your PCM audio, e.g. your mp3 or ogg files.
If you are inside a voice call (e.g. FSO/zhone), open amixer or load a state file with alsactl and change the following mixer controls:
UNKNOWN
Here is a state file that allows both recording and playback from and to a gsm call.
File: File:Callrec.txt
To record just issue:
arecord -D hw:0,0 -r 8000 -f S16_LE -c 2 record.wav
and to inject sound just issue:
aplay -D hw:0,0 record.wav
If you have any problems you can contact me on IRC, TAsn.
P.S There's a bug concerning the Right and Left mux, you have to change the left after you change the right, loading the state file may cause this issue to show, so just in case, I recommend appending:
amixer sset 'Capture Right Mux' 'Line or RXP-RXN'
amixer sset 'Capture Left Mux' 'Line or RXP-RXN'
to the alsactl -f Callrec.txt restore command.
For the actual recording: arecord -D hw:0,0 -r 8000 -f S16_LE -c 2 record.wav
please note that this is the state file I wrote for my Call Recorder, so if you need anything you might miss here, just go and check it's source.
The actual state for gsmhandset (gsmhandset.state): File:Callrec-gsmhandset.txt
A patch (diff gsmhandset.txt callrec-gsmhandset.txt) to apply on every state file, including gsmheadset.state and gsmspeakerout.state. File:Callrec-gsmhandset-patch.txt
The userspace sound control deamon might be a separate process or (more likely) part of some larger general hardware management daemon.
It will provide the following features:
In order to provide the desired functionality, the daemon first needs to be capable of doing audio playback.
If the user is listening to music on the headset, we want to mix the ring tones only into the headset audio, as we must not interrupt and play it on the speaker. Reason: headset can't be switched off during playback via speaker, so to avoid extremely loud headset playback there must NOT be any speaker playback while headset is inserted.
In expression: loading speakerout.state is deprecated while JACK_INSERT is asserted.