Freerunner Navigation Board v3
From Openmoko
The third version of the Freerunner Navigation Board was necessary because the compass chip used on the Freerunner Navigation Board and the Freerunner Navigation Board v2 has been discontinued.
Contents |
Features
Due to the new, smaller compass chip, the FRNBv3 offers a complete 10-DoF navigation solution. In addition to the 3D gyroscope, 3D compass and the barometer which are already known from the FRNBv2, the v3 adds a high resolution accelerometer. It should be more accurate for navigation purposes than the integrated LIS302 accelerometers.
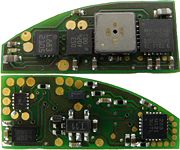
Top Side
- 3D Gyroscope ITG-3200
- 3D Magnetometer HMC5883L
- Air pressure/temperature sensor BMP085
- Accelerometer BMA180
Bottom side
The Bottom side of the PCB contains optional chips which might be used for different purposes. The FRNBv3 includes:
- TCA6705 7 channel LED controller
- MPR121 touch sensor controller
- M26LR64 I²C EEPROM accessible through RFID (antenna still needed)
- TXS0102 I²C level shifter (to connect additional sensors
- MIC1557 based 38KHz oscillator (for IR-remote control applications)
Additional features
The board operates with 3V or 3.3V which is needed for the sensors to work correctly. To be able to connect the board to other devices (for example GTA04, OpenPandora, Always Innovating devices), the I/O voltage can be anything between 1.8V and VCC. To use the board with the Freerunner, just short the VCC and VCCIO solder points.
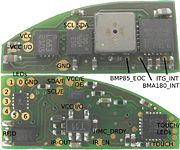
All sensors feature a "conversion complete" output which can trigger an interrupt. These signals are now available at small solder points.
Documentation
Schematic and board layout files are available from https://gitorious.org/frnbv3/frnbv3-hardware (CadSoft EAGLE 5.x format)
Pinout
Standard features
| Pin | Description | Voltage range |
|---|---|---|
| GND | Ground | 0 |
| VCC | Supply voltage for sensors. | 3 - 3.6 |
| VCC I/O | Interface voltage of the I2C bus. | 1.8 - VCC |
| SCL | I2C clock line | VCC I/O |
| SDA | I2C data line | VCC I/O |
Level shifter
| Pin | Description | Voltage range |
|---|---|---|
| VCC/E | Target (external) VCC | VCC - 5.5 |
| SCL/E | level translated I2C clock line | VCC/E |
| SDA/E | level translated I2C data line | VCC/E |
| OE | Output enable: connect to VCC I/O to enable the level shifter | VCC I/O |
Installation
See Freerunner Navigation Board v2
Power consumption
All sensors on the FRNBv3 support powermanagement. The current consumption of each sensor is listed in the table below. These values are taken from the datasheets, the real current consumption could be different. It often increases with higher sample rates.
| Sensor | standby | active | remarks |
|---|---|---|---|
| ITG3200 | 5µA | 6500µA | |
| HMC5883L | 2µA | 100µA | 7.5 Hz |
| BMP085 | 0.1µA | 12µA | average current in high resolution mode (default), 1 Hz |
| BMA180 | 0.5µA | 975µA | "low noise" mode |
The power state of each sensor can be controlled through the I2C bus. Most kernel drivers expose a sysfs file to change it. Integration with the generic linux powermanagement code is planned.
Issues
Known HW or SW Issues Nothing known yet.
Software
Availability
The handheld-linux.com team already takes preorders. You can find it here.
Two assembly options are available:
- Complete: Contains all chips as described above.
- Standard: Top-Side only, contains all sensors relevant for navigation purposes. The compass chip should be a little bit more accurate since a few capacitors on the bottom side are missing. They could distord the magnetic field.